November 6, 2020
Standard versus Ultrasound-Assisted Thrombolysis for Submassive Pulmonary Embolism
Presented by Efthymios Avgerinos, MD, PhD, MSc
Standard vs. UltrasouNd aSsisted cathEter-directed Thrombolysis in Submassive Pulmonary Embolism (SUNSET sPE) is a multicenter randomized trial that investigated whether ultrasound-assisted (USAT) is superior to standard-catheter (SCDT) thrombolysis in pulmonary arterial thrombus reduction.
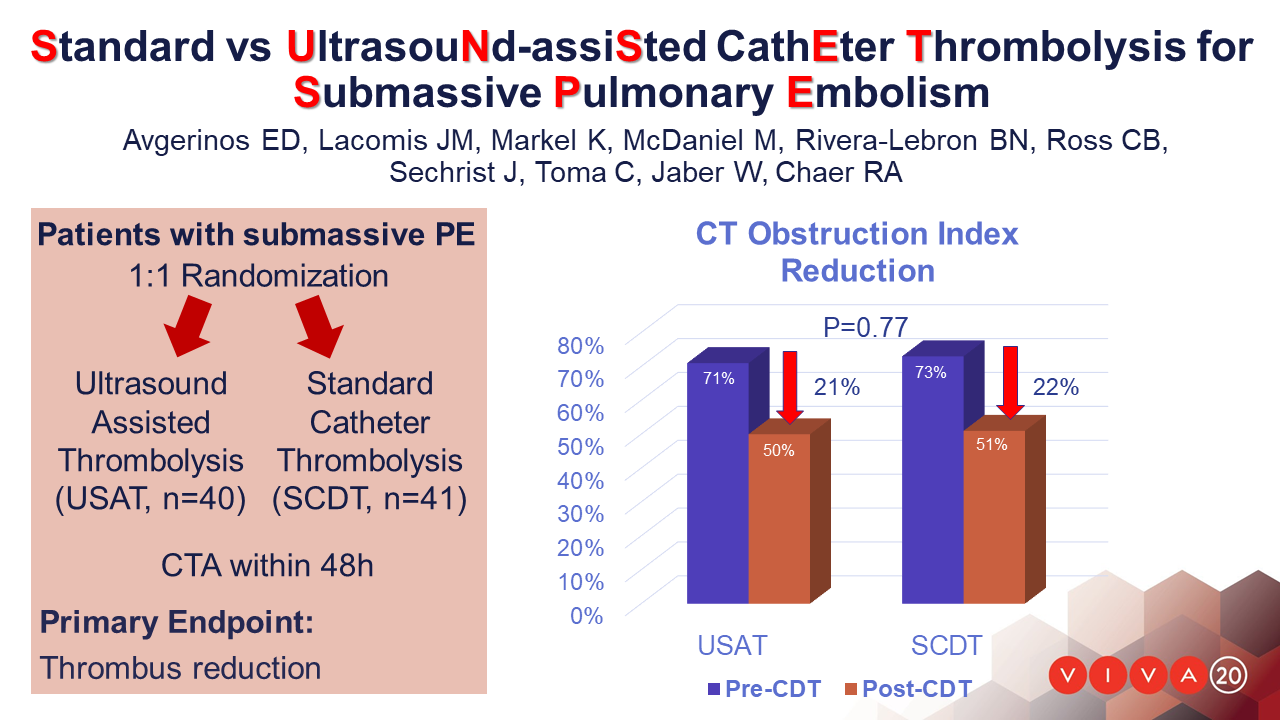
Adults with sPE were randomized 1:1 to USAT or SCDT. Thrombolysis dose and duration were left to the operators’ discretion. The primary outcome was 48-hour clearance of pulmonary thrombus assessed by pre- and post-procedure computed tomography angiography (CTA) using a refined Miller score. Secondary outcomes included right to left ventricular (RV/LV) ratio improvement, intensive care unit (ICU), bleeding and other serious adverse events.
81 patients with acute sPE were randomized and were available for analysis. Mean total dose of alteplase for USAT was 19±7mg and 18±7mg in SCDT (P=0.53) infused over 14±6hours and 14±5hours respectively (P=0.99). In the USAT group (n=39), the mean raw pulmonary thrombus score was reduced from 31±4 at baseline to 22±7 (P<.001). In the SCDT group (n=41), the score was reduced from 33±4 to 23±7 (P<.001). There was no significant difference in mean thrombus score reduction between the two groups (P=0.76). The obstruction index reduction was also similar between groups: 21% and 22% for USAT and SCDT, respectively (P=0.77). The mean difference in RV/LV ratio from baseline (1.54±.30 for USAT, 1.69±.44 for SCDT) to 48 hours was 0.37±0.34 in USAT versus 0.59±0.42 in SCDT (p=0.01). In 5 USAT and 3 SCDT patients there was no RV/LV ratio improvement. Major bleeding (one stroke with hemianopia and one vaginal bleed requiring transfusion) occurred in 2 patients both in the USAT group. The average ICU stay for the entire cohort was 3.2±6.3, similar between groups.
In the SUNSET sPE trial, patients undergoing USAT had similar pulmonary arterial thrombus reduction compared to SCDT, using comparable mean lytic dose and duration of lysis.
About VIVA Physicians
VIVA Physicians, a not-for-profit organization dedicated to advancing the field of vascular medicine and intervention through education and research, strives to be the premier educator in the field. Our team of specialists in vascular medicine, interventional cardiology, interventional radiology, and vascular surgery is driven by the passion to advance the field and improve patient outcomes. Educational events presented by VIVA Physicians have a distinct spirit of collegiality attained by synergizing collective talents to promote awareness and innovative therapeutic options for vascular disease worldwide. To learn more about VIVA Physicians, visit www.vivaphysicians.org.
SOURCE VIVA Physicians
For further information: press@vivaphysicians.org
